8 Life-Changing Benefits of Exercise for the Elderly
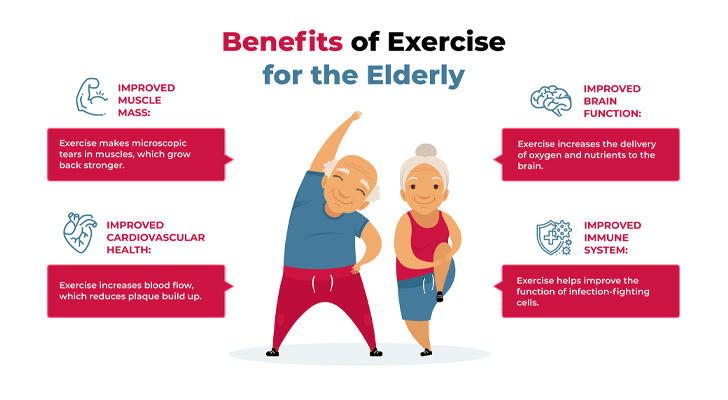
As we age, staying active becomes crucial for maintaining health, energy, and happiness. Exercise can help counteract the natural decline in body functions, rejuvenating the later years of life. This article highlights eight key benefits of exercise for older adults and provides practical advice for incorporating it into daily routines.
1. Improve Cardiovascular Health
Good cardiovascular health is vital for older adults. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming, strengthens the heart, improves blood flow, and helps lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. This reduces the risk of heart disease and stroke. Exercise also helps keep blood vessels flexible, preventing artery hardening.
Practical Tip: Start with activities like walking or swimming and gradually increase the duration and intensity. Always consult with a healthcare provider before beginning a new exercise program.
2. Enhance Musculoskeletal Strength
Aging often leads to reduced muscle mass and bone density, increasing the risk of conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis. Exercises such as strength training, yoga, and Tai Chi help build muscle, improve bone density, and increase joint flexibility. This reduces the risk of falls and fractures and enhances overall mobility.
Practical Tip: Incorporate strength training using light weights or resistance bands, and practice balance and flexibility exercises like Tai Chi. Joining a class can ensure proper technique and safety.
3. Better Balance and Coordination
Poor balance is a common issue for older adults and a major cause of falls. Balance exercises, such as standing on one foot or walking with eyes closed, along with coordination activities like Tai Chi or dance, can greatly improve balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls.
Practical Tip: Include balance and coordination exercises in your routine. Consider activities like Tai Chi, which are specifically designed to enhance these skills.
4. Enhance Cognitive Function
Exercise is beneficial for brain health. It boosts blood flow to the brain, supports neuron connections, and enhances cognitive functions. For older adults, this can help delay memory loss and lower the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Practical Tip: Engage in regular aerobic exercises and combine them with mentally stimulating activities, such as puzzles or learning new hobbies, to support cognitive health.
5. Strengthen the Immune System
A strong immune system helps the body fight off illnesses. Regular exercise improves immune function by activating immune cells and enhancing overall immune response. It also supports metabolism and helps remove toxins from the body.
Practical Tip: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Activities like brisk walking or cycling can boost immune function.
6. Improve Mental Health
Exercise has a positive effect on mental well-being. It triggers the release of endorphins, which help reduce stress and anxiety, and promote feelings of happiness. Additionally, regular exercise can boost self-esteem and provide a sense of accomplishment.
Practical Tip: Choose enjoyable activities, such as group classes or outdoor walks, to make exercise a fun and rewarding experience.
7. Enhance Social Interaction
Group exercise classes offer a valuable opportunity for social engagement. They allow older adults to meet new people, build friendships, and enjoy the social aspect of exercise. This helps combat feelings of loneliness and fosters a sense of community.
Practical Tip: Join community exercise groups or classes to benefit from social interactions and shared experiences.
8. Improve Sleep Quality
Good sleep is essential for overall health. Regular exercise helps regulate sleep patterns and improves sleep quality. It makes falling asleep easier and promotes deeper, more restful sleep.
Practical Tip: Finish exercising a few hours before bedtime to allow your body to relax. Gentle activities like stretching or yoga can also aid in better sleep.

Case Study: Grandma Wang’s Exercise Journey
Grandma Wang, a 70-year-old retired teacher, experienced a significant setback after a fall and broken leg. Concerned she might never walk independently again, she joined a Tai Chi class in her community. Initially, she felt tired from her lack of activity, but over time, she adapted and noticed improvements in strength and balance. The social support from the class also enhanced her mood and overall happiness.
After more than two years of consistent exercise, Grandma Wang’s physical condition greatly improved. She regained her ability to walk and actively participate in social activities. Her story highlights how exercise can transform both physical health and overall well-being, adding joy and vitality to later years.
Conclusion
Exercise offers numerous benefits for older adults, affecting physical health, mental well-being, and social connections. Regular activity improves cardiovascular health, musculoskeletal strength, balance, cognitive function, immune response, mental health, social interaction, sleep quality, weight management, and independence. Encouraging older adults to incorporate exercise into their lives, providing practical advice, and ensuring professional guidance can help them enjoy a healthier and more fulfilling life.
